2FA
Traditional usernames and passwords are no longer enough to protect your business from cyber threats. Passwords can be stolen through phishing, malware, or even simple human error. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of protection, making it much harder for attackers to access your data and systems.
While some may view 2FA as an extra step, the reality is that it has become essential in today’s digital landscape to secure business accounts, sensitive data, and remote access systems.

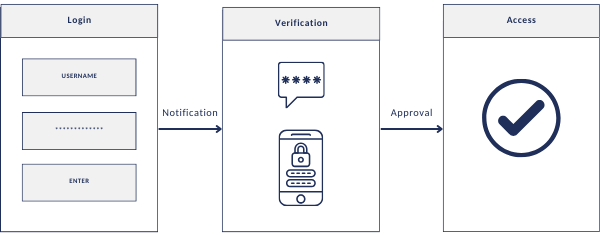
Two-Factor Authentication, or 2FA, requires users to provide two types of verification before they can access an account. The first factor is something you know, such as your password. The second factor is something you have, like a code sent to your phone or generated by an app.
Even if someone steals your password, 2FA makes it extremely difficult for them to break into your accounts. It’s one of the most effective ways to protect against unauthorised access and data breaches.
There are several ways to implement two-factor authentication, depending on your business needs:
An authenticator app provides a secure way to verify your identity, either by generating a time-based code on your phone or by sending a verification prompt that you approve in the app. This method is highly secure because the verification happens on your device and cannot easily be intercepted
A one-time password (OTP) is sent via text message to your phone. It’s simple to use and widely adopted, but slightly less secure than an authenticator app.
A code or verification link is sent to your email address. While easy to implement, email-based 2FA is more vulnerable, so we recommend pairing it with other methods for stronger security.
Reduces the risk of cybercriminals breaking into your accounts.
Protects against phishing, credential theft, and brute-force attacks.
Helps meet cybersecurity and data protection requirements.
Works with cloud platforms, VPNs, and remote access tools.
Minimal disruption to users while greatly improving security.
